Nearly every aspect of our lives is online, from applying to jobs and going to school to ordering toothpaste and planning parties. With so much of our personal information on our devices, protecting them from cyberattacks is essential.
You might think that entering your first and last name on a survey is innocent, but what if it’s compromised or fake? Or, that seemingly harmless download or click on an email could give hackers access to your personally identifiable information, which can affect you for years.
That’s why our cybersecurity team put together this list of 25 cybersecurity tips you can use to minimize your digital risks. Don’t feel pressured to implement them all at once though. Our motto for information security is “progress, not perfection.”
Cybersecurity Tips
While some of these tips are a one-time thing, some are best practices to adhere to on a consistent basis. Let’s get started on improving your digital security.
Software Updates
As soon as you get notified about software updates for your operating system, perform them, as they contain the latest security patches. Here’s how to do it on the most popular types of devices:
iPhone
- Select Settings.
- Click General.
- Click Software Update.
- Select Download And Install.
- Select Install.
- Enter your iPhone passcode.
Android
- Go into your phone’s Settings.
- Select System.
- Select Advanced.
- Select System Update.
Mac
- Open the System Settings app.
- Click Software Update.
- If there are any updates, click Update Now.
- Enter your administrator password.
PC
- Open Internet Explorer.
- Select Tools.
- Select Windows Update.
- Select Microsoft Update.
- Click Try Microsoft Update Today.
- Click Start Now.
- Click Continue.
- Read the license agreement. A Security Warning box will appear.
- Select Install.
Pro Tip: Change your settings so that software updates happen as soon as they’re ready; that way, you won’t have to perform updates manually whenever they’re available.
Antivirus Software
Do you need antivirus software? The answer depends on what type of device you have, but usually, it’s a resounding yes. While iPads and iPhones don’t need antivirus software, Windows 10 needs antivirus, Macs need antivirus, and Chromebooks need antivirus.

Antivirus scans for different types of malware including ransomware and spyware. Look for antivirus software with a firewall to protect your network from cyber threats as well.
Password Hygiene
Like physical hygiene, password hygiene is as important as it is elementary, yet it’s often forgotten. Rather than using the exact same password for all of your online accounts, make sure each one has a unique, strong password. Follow these password tips:
- Use 12 to 16 characters.
- Use letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Don’t include any personal information.
- Don’t use repeating characters.
- Store all of your passwords in a password manager, like 1Password.
>> Keep Reading: Our Favorite Password Managers of 2025
Authentication
Whenever possible, add two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) to your accounts. This will require you to enter either an additional passcode sent to your phone or fingerprint/facial recognition. Learn more in our guide to authentication.
Phishing Scams
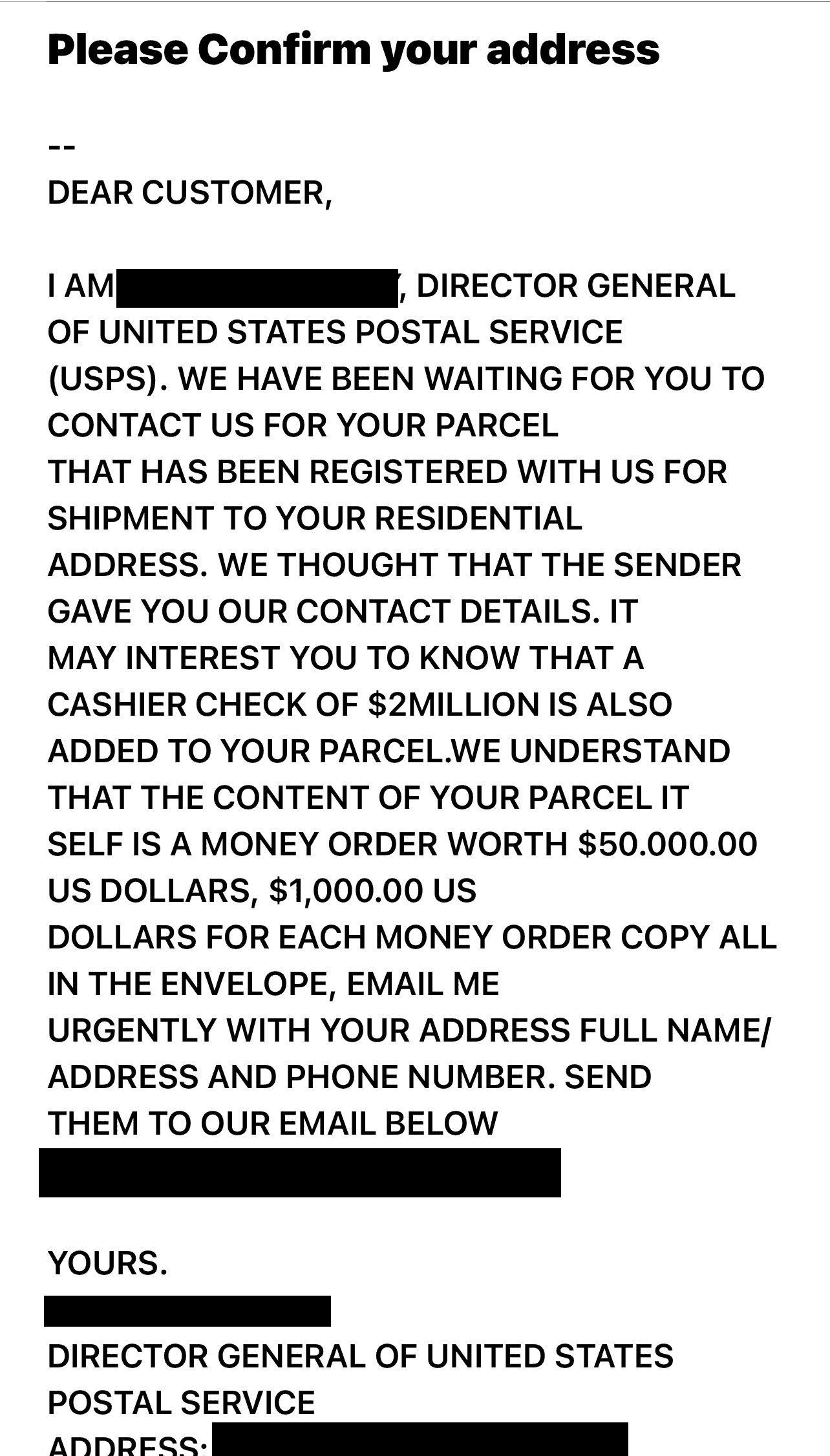
Phishing is one of the most common ways that hackers obtain another user’s credentials to steal their identities. Most antivirus programs contain protection against phishing, but if you’re not sure, it’s best not to click on any unfamiliar emails, texts, messages, attachments, or links. These links could bring you to fraudulent websites for social engineering. That’s how hackers get your login credentials directly from the source (you).
Did You Know: Phishing doesn’t just end at emails. Hackers have found ways to scam people through phishing text messages, too. Read our guide on “smishing” to keep your device secure.
Personally Identifiable Information
Personally identifiable information, or PII, includes sensitive data such as:
- Your name
- An email address
- A mailing address
- A phone number
- Your Social Security number
Hackers can use other people’s PII for identity theft, which is why it’s important to protect your identity by not sharing your PII, especially on social media. Have you ever Googled yourself? You might see a ton of PII come up on the first page. Learn how to check if your identity has been stolen and delete your PII from Google.
Note: According to our research on sharenting, a term for parents sharing on social media, over 80 percent of parents use their children’s real names in posts, putting them at risk for child identity theft.
Mobile Devices
When thinking about cybersecurity, sometimes we only consider our computers and not our mobile devices like our smartphones. That’s a huge mistake. Here’s how to protect your smartphones from cyber attacks:
- Use passcodes. To prevent our iPhones from being hacked, we set up six-digit passcodes that we enter every time we unlock our phones (that is, if Touch ID isn’t working). Passcodes prevent you from ever having to ask “What do I do if my phone is hacked?” Here’s how to set them up on iPhones and Androids:
iPhones (X or later)
- Select Settings.
- Select Face ID & Passcode.
- Select Turn Passcode On.
- Enter a six-digit passcode.
- Enter the passcode again to confirm and activate it.
Androids
- Enter your phone’s Settings.
- Select Security.
- Select Screen Lock.
- Select Standard Locks.
- Choose Password.
- Enter more than four characters.
>> Related Article: Best Password Managers for Android
- Disable Wi-Fi. Joining public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN (virtual private network) isn’t safe, as your web activity and IP address are exposed. Here’s how to turn off Wi-Fi on your phone:
iPhone
- Select Settings.
- Select Wi-Fi.
- Toggle Wi-Fi off.
Android
- Swipe down on your Android screen.
- Touch and hold Wi-Fi.
- Turn off Use Wi-Fi.
- Disable location sharing. Does the Panera app really need to know your whereabouts at all times? For most people, the answer is no. Keep your location to yourself by taking the following steps:
iPhone- Select Settings.
- Select Privacy.
- Select Location Services.
- Toggle off Location Services.
Android
- Swipe down on your Android screen.
- Touch and hold where it says Location.
- Select Advanced.
- Select Google Location Accuracy.
- Turn off Improve Location Accuracy.
- Disable Bluetooth. We love using Bluetooth to connect to our AirPods, our Nest Mini smart speaker, and a ton of other smart home devices. However, hackers can exploit Bluetooth vulnerabilities to spread malware, so turn it off by default on your smartphone. Here’s how:
iPhone- Go to Settings.
- Select Bluetooth.
- Turn the toggle off.
Android
- Select on Settings.
- Select Connected Devices.
- Select Connection Preferences.
- Select Driving Mode.
- Select Turn On Automatically.
- Select Advanced.
- Turn off Turn On Bluetooth Automatically.
Backup Data
For the most security, don’t store all of your files in encrypted storage. Rather, use encrypted cloud storage like ProtonDrive, Sync, or Tresorit.
VPNs
Public Wi-Fi networks are convenient ways to get on the internet when you’re standing in line or working in a cafe, but they’re also not the most secure. When you’re on a public Wi-Fi network, everyone can see what you’re doing online as well as your device’s private IP address.
On the other hand, VPNs hide your browsing history, changing your IP address so you can remain anonymous online. Learn how to set up a VPN, or read our VPN guide for more information on how VPNs encrypt data.
Credit Reports
Credit reports are one of those boring adult topics that immediately cause our eyes to glaze over. However, monitoring your credit through a credit reporting service or identity theft protection with credit monitoring is a great way to prevent identity theft. See if there are any unfamiliar accounts, loans, mortgages, etc., on your credit report, as these could indicate identity theft. You can even get a credit report for free!
>> Read Next: Best Identity Theft Protection with Fraud Detection
Access Control
If you’re in charge of the IT of a business, consider who can gain access to certain computers with sensitive information. Digital security doesn’t just end at the devices themselves. Rather, you need to physically secure these devices with locks, passcodes, and business security systems.
Network Monitoring
To monitor for threats across your entire network, install antivirus software with a firewall.
Employee Training
It isn’t enough to program and protect devices. Inexperienced employees cause most phishing attacks. Train your employees on how to recognize phishing messages, among other things. We recommend distributing written policies telling employees to:
- Put away files.
- Log off devices.
- Never leave devices unattended.
- Don’t store personal information on work devices.
- Only use work devices for business use.
- Lock offices and filing cabinets.
Protected Servers
If you have a data server, be sure to store it in a locked room with passcodes. Physical access to servers is one way that data breaches can occur.
Cyberbullying
Unfortunately, cyberbullying is prevalent in the U.S., particularly for kids ages 10 to 18. Our research on cyberbullying found that 1 in 5 children have been victims. If someone is cyberbullying you, don’t respond. Instead, block them and let an adult know (assuming you’re a minor).

DDoS Attacks
DDoS stands for Distributed Denial or Service, and it’s a cyberattack that forces people offline. By flooding networks with requests and traffic, hackers break down sites until they can’t accept legitimate traffic.1 However, by hiding your IP address, VPNs can stop DDoS attacks by making your network harder (but not impossible) to locate.
Disposing Of Electronic Devices
Getting rid of your old iPhone? Be sure to perform factory resets on your devices before throwing them out. This will wipe your device back to the settings it had when you got it, deleting any and all of your PII. After backing up what you need, here’s how to factory reset your device:
iPhone
- Go to Settings.
- Click General.
- Click Reset.
- Click Erase All Content And Settings.
- Enter in your passcode or Apple ID password.
Samsung Android version 5.0 or above
- Click Apps.
- Click Settings.
- Click Backup And Reset.
- Choose Factory Data Reset.
- Choose Reset Device.
- Click Erase Everything.
Mac
- Turn on your computer.
- Once you see an Apple logo or another image, press and hold the Command and R keys.
- Select your user interface, and enter the administrative password.
- In the Spotlight feature, type in “Disk Utility.”
- Open the Disk Utility app.
- Select Macintosh HD.
- Click Erase.
- Type in Macintosh HD as the name, and APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled) to the format.
- Click Erase Volume Group or Erase.
- Enter your Apple ID.
- If there are any more internal volumes in the sidebar, click on each and select the delete button in the tool button.
- Quit Disk Utility.
PC
- Click Settings.
- Click Change PC Settings.
- Click Update And Recovery.
- Click Recovery.
- Click Remote Everything And Reinstall Windows.
- Click Get Started.
- Follow the rest of the instructions, choosing to Erase Data Thoroughly.2
Securing IoT Devices
Do you live in a smart home with convenient home automation? If so, make sure you secure your home, your Internet of Things (IoT) devices in particular. Protect them with unique passwords and authentication whenever it’s available. You can even set up a VPN on a router to encrypt all of the IoT devices on your network.
Child Safety Online
There’s a lot that goes into keeping kids safe online. You can use parental control software, for example; that’ll tell you what they’re doing online. Software apps can also restrict certain websites and search terms, and they can enforce your limits on screen time. Also, to keep kids safe on laptops, you can have them use them in public areas only so you can see what they’re doing online. For the most protection, subscribe to identity theft protection for families.
Public Charging Stations
One of the joys of the 21st century is being able to charge your phone on the sidewalk through public charging stations. But like most convenient things, public charging stations have their drawbacks in the name of digital security.
The issue is that the USB drives you use to connect your device not only transmit power, but also sensitive data. That makes it easy for someone to “juice jack,” or access your phone’s data and run malware. Here are your options for using public charging stations safely:
- Use an AC outlet. AC outlets only transmit power, not data.
- Use a charge-only USB adapter or a USB data blower. This will block the data and only transmit the power.
Safe Online Shopping
So you were scrolling Instagram when you saw an ad for unrippable tights. Before you enter in your credit card information, check that the business is legitimate through the Better Business Bureau.
You should also pay with apps like Paypal, which don’t give the vendor your financial information. Plus, PayPal Purchase Protection means that if the item doesn’t come or isn’t as it was described, you can get a full refund. PayPal protects sellers, as well, making it a win-win.3
Securing Remote Workers
Even before the COVID-19 pandemic forced us to stay at home, many employees worked remotely from their homes. But how can you work from home safely? For most people, you’ll follow the same tips as you would in person, i.e., logging off devices, locking them up once you’re done for the day, etc. But working from home requires a few more best practices, including:
- Don’t let your family use your devices, no matter how much they beg. After all, you love them, but they don’t necessarily have your solid understanding of digital security.
- Cover your webcam. This is necessary for privacy, especially if you use Zoom or work in your bedroom.
- Protect your home Wi-Fi network with a password; this will also prevent your nosy neighbor from hopping on your Wi-Fi and slowing down speeds.
- Use a VPN for businesses. Each employee has their own home network, which may or may not be secure.
- Install antivirus software for businesses on all work devices.
Turn Off Autofill
Autofill, another convenient feature that can be dangerous if it gets into the wrong hands. Although it certainly makes filling out forms less soul sucking, if you lose your phone, autofill could hand over your PII to anyone with access. Here’s how to turn it off on Safari, the default browser on iPhones and Macs; Chrome, the default on Androids; and Internet Explorer 11, the default on PCs.
iPhone
- Click Settings.
- Click Safari.
- Turn off AutoFill Passwords.
Android
- Open the Google app.
- Tap More.
- Tap Settings.
- Tap General
- Turn off Autocomplete With Trending Searches.
Mac
- Open Safari.
- Click Preferences.
- Click AutoFill.
- Uncheck all the boxes next to AutoFill Web Forms.
PC
- Open Internet Explorer 11.
- In the taskbar search bar, type Internet Explorer.
- Click Internet Explorer.
- Click Tools.
- Click Internet Options.
- Go to the Content tab.
- Under AutoComplete, click Settings.
- Uncheck all the boxes.
- Check OK.
Pop-Ups
Pop-ups are the cockroaches of the internet world, but if you’re getting more than usual, it may be a sign that you have adware on your device. Adware is a potentially unwanted program (PUP) that makes money by displaying ads on your device, as well as tracking your browsing, selling this data to third parties so they can create targeted ads. Don’t click on pop-ups, and learn how to remove adware from your devices.
Check URLs
Not sure if a URL is legitimate or not? Google has a tool that lets you check if a site is safe simply by copying and pasting the URL into its safe browsing site status bar.4
Use HTTPS
When in doubt, look for URLs that start in HTTPS, not HTTP. What’s the difference?
HTTPS has more layers of security. It uses SSL, a Secure Sockets Layer Protocol that encrypts all the communication between your browser and the website you’re on. HTTP lacks SSL, making it less secure.5
Why Does Cybersecurity Matter?
We know that data security is important, but you may not know why. Now, we’re not trying to scare you, but insecure devices can have major consequences.
The Consequences Of Security Breaches And Hacks
- Identity theft: Identity theft means that someone gains hold of your PII and uses it to take out loans, commit crimes, or use your credit cards, all in your name.
- Account takeovers: Account takeovers happen when someone, well, takes over your accounts. According to our research, 51 percent of accounts taken over are social media, the majority, while another 32 percent are banking accounts.
- Financial losses: Whether you’re a business or an individual, cyberattacks and hackings can lose you money. In 2020, the average cost of a data breach in the U.S. was $3.86 million, according to IBM’s annual Cost of a Data Breach Report.
- Loss of productivity: On average, it took businesses 280 days to identify and contain data breaches in 2020.6
- Loss of reputation: For businesses, a data breach is bad for PR.
- Loss of customers: You may also lose customers if their data is exposed.
- Lack of privacy: Unlike monetary losses, data privacy is priceless, especially when tech companies keep user data in droves.
- Lost access to cryptocurrency: Got Bitcoin stored digitally? Losing your password may mean losing access to your money; in fact, in our cryptocurrency research, we found that 25 percent of crypto owners have had issues accessing it. For about half of these incidents, the cause was a lost or forgotten password. Yikes.
- Decreased credit scores: If you have your identity stolen, that could lower your credit score, making it harder to get loans, jobs, and rental agreements.
What Causes Business Data Breaches?
Even with the most careful digital security practices, if a business has a security breach, it’s out of your hands. The causes of security breaches include:
- Physical access
- Bad passwords
- Hacking
- Phishing
Recap
With so much of our personal information online, safeguarding it against cyber threats is crucial. Data breaches are not uncommon, and when they do happen, it can lead to spam, financial loss, fraudulent activity, and identity theft. Even doing something as seemingly harmless as clicking on a link can expose you to malicious activity online.
However, by practicing good digital hygiene you can greatly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to hacking, data breaches, and other cyberattacks. Performing software updates and using antivirus software require minimal effort, but are extremely helpful. You should also use strong passwords, implement multi-factor authentication, and stay vigilant about phishing scams.
Once you have the basics down, start disabling unknown or unnecessary Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connections, avoiding public networks, not reviewing sensitive data while on a hotspot, and securing IoT devices to enhance your security further. Of course, cybersecurity issues can still happen, but by following our advice, you won’t go in blind.
FAQs
Cybersecurity is such a huge topic that we receive dozens of questions about it per week. We’ve decided to answer them here.
-
How do you maintain cybersecurity?
You can maintain your cybersecurity in many ways, including:
- Use VPNs on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Install antivirus software on your devices.
- Use identity theft protection services.
- Use secure passwords by checking them with a password strength checker.
- Don’t jailbreak your phone if you have an Android.
-
What are the 10 steps to cybersecurity?
There are more than 10 steps to cybersecurity, but here are some of the most important steps:
- Add two-factor authentication or multi-factor authentication to online accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Don’t click on unfamiliar messages, as these could be phishing attacks.
- Don’t share your personally identifiable information (PII) online.
- Create a passcode on your mobile device.
- Don’t join public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN.
- Disable Bluetooth when you’re not using it.
- Turn off location sharing.
- Backup your data in encrypted cloud storage.
- Factory reset your devices before you dispose of them.
- Only use public charging stations with either an AC outlet, a USB data blocker or a charge-only USB adapter.
-
What are some cybersecurity best practices?
Some cybersecurity best practices are:
- Turn off autofill on your devices.
- Turn on the “find my phone” feature.
- Have your phone lock after a certain period of time.
- Use Paypal for online shopping.
- Check if e-commerce businesses are legitimate with the Better Business Bureau before buying anything online.
-
How can I reduce cyberattacks?
To reduce cyberattacks, we recommend using antivirus software. Antivirus software scans devices for suspicious behavior. If it finds anything suspicious or malicious, it quarantines it in a sandbox, where it can’t harm the rest of your device.