Using a VPN is one of the easiest, most straightforward ways to enjoy safer browsing. Typically, you launch the VPN app, find a good server, and hit that “connect” button. And just like that, your connection is secure.
But what would you do if your VPN stops working? Or if you’re forever stuck in the “connecting” state? Or what if you just can’t get the VPN app installed in the first place?
We’ve been in those situations, too, pulling our hair out trying to figure things out. So, in this guide, we’ll tackle the most common VPN issues and show you how to fix them like a pro.
Why VPNs Malfunction
As user-friendly as VPNs may be, there’s an intricacy in how they function. They are like a virtual car engine – easy to switch on and off. However, if you look under the hood, you’ll see a lot of moving components.
Any of those parts can malfunction and cause your VPN to stall. There could be an issue with your network or firewall, your device, or the VPN app. Some issues may even be caused by things beyond our control, such as when there’s a server or maintenance issue or when the VPN infrastructure is down.
Here are some of the most common reasons why a VPN might malfunction:
- Internet Connection Issues: If you have an unstable internet connection, your VPN might have issues maintaining a connection. Some ISPs also throttle VPN traffic, which can lead to poor performance or drops in your connection.
- Software and Configuration: If you’re using an outdated version of a VPN client, that can lead to malfunctions and issues with compatibility. Having the wrong settings in the VPN client can also cause malfunctions.
- Server Problems: When there are too many users on one VPN server it can get overloaded. That will cause slowdowns and drops in connections.
- Firewall and Security Software: If you have a firewall or antivirus program installed, your device might block a VPN connection.
- Protocols: Depending on the network, a VPN protocol might not be supported. That means a network might block certain protocols causing your VPN server and client connection to fail.
- Restrictions around Geolocations: Sometimes a website or service will purposefully block an IP address associated with a VPN.
- Operating System Issues: Some VPN clients are simply not compatible with certain operating systems.
- DNS Leaks: Not configuring a VPN correctly will cause your DNS queries to leak, which can lead to VPN malfunctions and also cause privacy and security issues.
>> Read Next: WebRTC Leaks: A Complete Guide
The best way to troubleshoot a VPN issue is to find out what’s causing the problem first. Once you do that, fixing your VPN will be a breeze.
Here are five of the most common VPN issues and how to troubleshoot and fix them.
Need a VPN You Won't Have to Fix?
Troubleshooting is a massive pain, especially when it comes to tech products. So why not choose a VPN that won't need fixing in the first place? Here are three options that we've personally tested and found to run like clockwork:



1. VPN App Won’t Install
The VPN app is your gateway to the VPN service itself. You’ll use it to select a server, connect to the VPN, and configure your connection settings, among other things. Sometimes, however, setting up a VPN app doesn’t go as smoothly as expected. So what could be the problem?
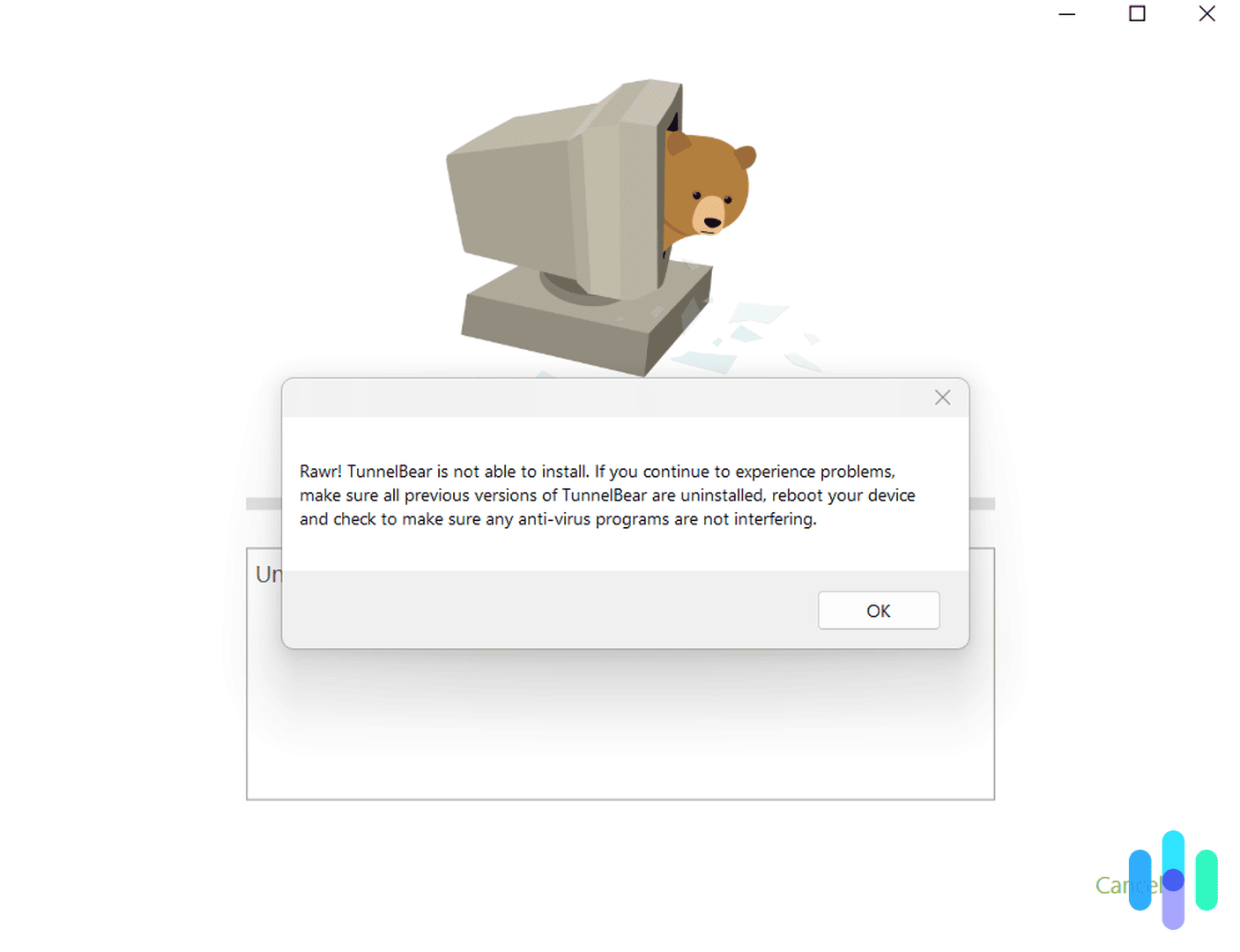
If you downloaded the app from a legitimate source, the problem is likely with your device. You may be missing a network adaptor, your firewall may be blocking the installation, or another program may be interfering.
Installation issues often occur on Windows, macOS, and Linux, and the solution can be simple. Before anything else, try these fixes:
- Restart your device, and then try again.
- If you’re using antivirus software, disable it temporarily. It could be interfering with the installation. Learn how to turn off antivirus software here.
- Check and update your network drivers. On Windows, you can do this in the Device Manager section of the Control Panel. On macOS, simply check if a software update is available, as macOS handles all driver updates.
- Go to your device firewall settings, and disable the firewall temporarily. It could be blocking the VPN app.
- Check the apps installed on your device. An older version of the VPN app may have already been installed or a previously uninstalled version may not have been removed properly.
- Check that the VPN installer is compatible with your device. Check the app’s system requirements, for example. If you are using a Windows computer, choose the right installer (32-bit or 64-bit) for your operating system.
Sometimes, installation issues can also come from the VPN app side. Newly- released and beta versions are often unstable, so if you still can’t install the app after trying the suggestions above, try downloading an older version. You can often find one of those in the VPN provider’s downloads page.
Pro Tip: If your iOS or Android VPN app won’t install, the problem is likely with Google Play or the App Store. Smartphone app downloads are managed by Google and Apple.
2. VPN Won’t Connect
Another common issue you’ll likely encounter at least once is a VPN that won’t connect. This issue is a bit more complex, and the culprit can be anything from your router to your app’s configuration.
Here are some things to try:
- Restart your device and the VPN: Ah, the classic “Have you tried turning it off and on again?” You’d be surprised how many issues restarting your device can fix. It’s almost always the first thing you should try. In addition to restarting your device, though, you should also restart the VPN. You may even want to log off and on for good measure, just in case it’s just a simple account syncing problem.
- Check your firewall: Your device’s firewall is its network defense, and it’s possible that it’s flagging down your VPN’s attempt to connect. To see if that’s the case, try disabling the firewall. If it works, you need to give the VPN access permission from your firewall settings.
- Test your internet connection: Another possible cause? Internet connectivity issues. See if you can access any website at all. If you can’t, that means your VPN is unable to connect because there’s a network interruption. Try restarting your router or calling your internet provider.
- Try a different network: If none of the above works, then the issue is most likely in your network itself. Try connecting your device to a different network, such as a mobile hotspot. If the VPN connects successfully, then you know that your network is the problem. Unfortunately, there’s a number of possible culprits, so you’re better off contacting your VPN tech support. They are better equipped to provide network-specific solutions.
3. Slow Internet Speeds
One of the most frustrating VPN issues of them all is a painstakingly slow VPN connection. Our VPN speed tests revealed that VPNs have gotten a lot better at delivering high-speed connections – at least that’s the case for the best VPNs out there. Yet, we still encounter slow speeds occasionally. How do you fix it?
Follow these three steps:
- Disconnect the VPN.
- Restart the VPN app.
- Connect to a different server than the one you connected to previously.
Most of the time, that will fix the issue. If it doesn’t, there are three more things to try.
First, use a different VPN protocol. You can find this in the VPN’s settings page. OpenVPN is likely going to be the default, so choose WireGuard if it’s available or any other VPN protocol if it’s not.
Second, choose another VPN server. Outages and server maintenance can affect entire regions, so if you’re connected to a U.S. server, for instance, try a U.K. or Australia server.
Third, restart your router. It’s possible that the culprit is your internet connection itself, so take a speed test to see if your network speed is normal. If it’s not, contact your internet provider.
FYI: A number of factors can affect your VPN internet speed, such as your proximity to the server, the number of users connected to the VPN, and the amount of traffic the VPN server is handling.
4. VPN Failing to Change Your IP Address Location
Perhaps you’re using a VPN to change your IP address and bypass geographic restrictions, such as to access a different Netflix region. The connection is successful, but you’re still finding yourself browsing your home region’s Netflix. That could be a case of a leaking IP address – either a DNS leak or a WebRTC leak.
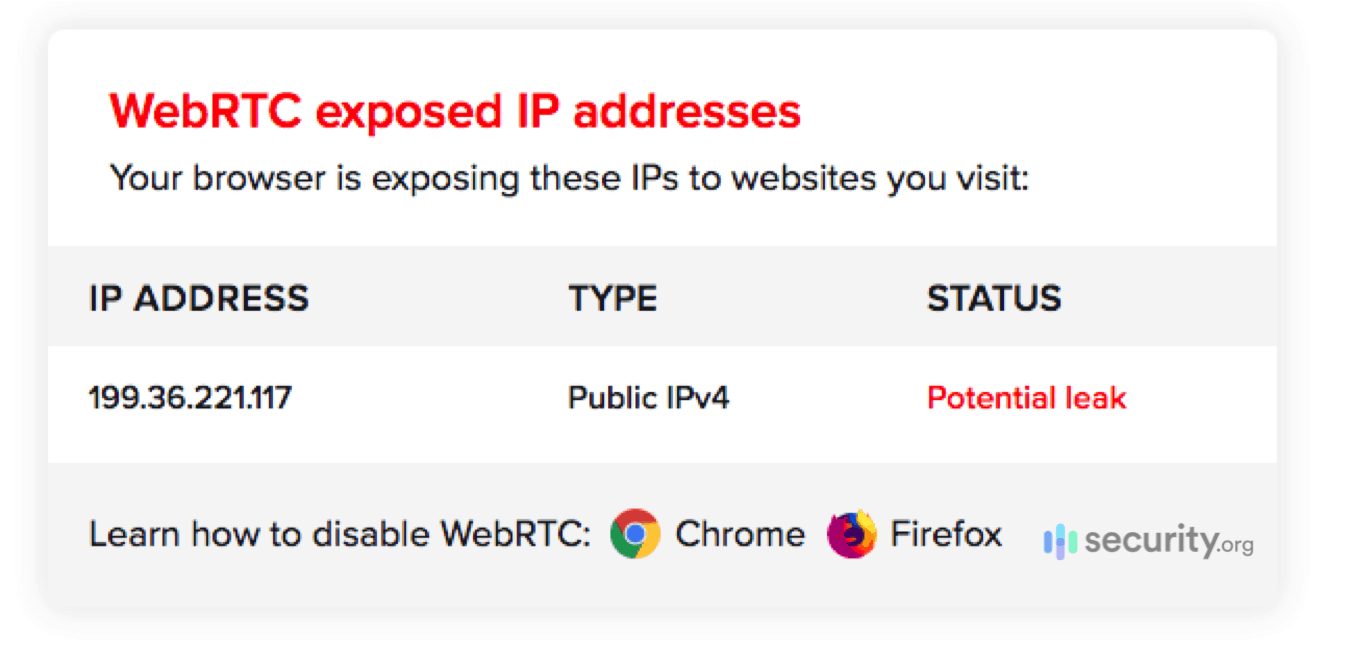
If your VPN is leaking your IP address, that means it’s not doing a good job of hiding your IP address. This doesn’t always mean that the VPN is unreliable. Perhaps there was just a mistake in the networking, so the first thing you should try is to change VPN servers.
After changing servers, use an IP address leak test to see if your VPN has changed your IP address location. There are many free tools available online. If the result comes back with your real location, then it’s time to try a different VPN provider. Your current VPN is leaky. If it comes back with the VPN server’s location, that means the VPN has hidden your real IP address location. Go back to Netflix. It should work now.
Pro Tip: IP address leaks are dangerous, as they can compromise your privacy, even if you’re connected to a VPN. If you find that your VPN isn’t protecting your IP address enough, it’s best to switch VPN providers.
5. VPN App Crashes
Lastly, some VPN apps have a tendency to crash. The cause is almost always the VPN app itself, so here’s what you should do.
First, restart the app. Second, look up if there’s a new software version. Your app may be outdated. If there’s none, try uninstalling and reinstalling the app.
If your VPN app still crashes frequently even after trying those fixes, then it might be a device issue. If you’re using a device that has seen better days, close all the other apps and background processes. Your device may be unable to handle multiple apps, causing the VPN app to crash.
Another thing to look into is if there’s malware on your device. There are types of malware that overclock CPUs to force apps to crash, such as rapidly replicating computer worms. The best thing to do if you suspect your device has malware is to run an antivirus scan.
Final Words
No VPN is perfect. You’re bound to encounter issues sometimes while using tools as complex as VPNs, so knowing how to troubleshoot and fix the most common VPN issues is important.
That being said, some VPNs are known to be more reliable than others. If you’re yet to purchase a VPN, check out our VPN comparisons and our VPN buying guide.
FAQs on Troubleshooting VPNs
We may have addressed the most common VPN issues, but let’s discuss some other VPN issues and possible fixes in this section.
-
Why is my ping always too high?
Your ping or latency when connected to a VPN is a product of several factors, but the easiest fix is to connect to a server closest to you. Your ping is high because data transfer between your device and the internet is taking too much time. Connecting to a nearby server reduces the travel time and, thus, improves the data transfer rate.
-
Why can’t I access websites while connected to a VPN, but other websites are working properly?
The reason for this is likely that the website is not available in the VPN server location. If you connect to a U.K. server, for example, the websites you visit will think you’re browsing from the U.K., even if you’re in the U.S. If you find that you can’t access a website, it’s likely that the website is blocking traffic from other countries.
-
My VPN speed is good, but why can’t I stream videos?
Your network uses different ports for different types of data, including video streams. It’s possible that your VPN doesn’t have access to that port in your home network.
-
Why can I no longer connect to the internet after disconnecting the VPN?
The most likely culprit is the VPN feature called a kill switch. Some VPNs have a kill switch that prevents devices from connecting to the internet whenever the VPN is switched off. You can simply go to your VPN app and disable the kill switch feature from the settings if you prefer not to use the feature.
-
What should I do if I’m unable to torrent while using a VPN?
Not all VPNs are torrent-friendly, and those that are usually require a special configuration in order to receive and send torrent streams. If your VPN is torrent friendly, try connecting to a P2P (port-to-port) or a torrent-optimized VPN server.